Hybrid Energy System
Provide an important opportunity for the active involvement of each single citizen (Green New Deal)
Hybrid Energy System
Manage multiple types of generation sources and/or energy storage systems of several different technologies
Hybrid Energy System
Enable an end-user aggregate management model such as a Renewable Energy Community (CER)
The project
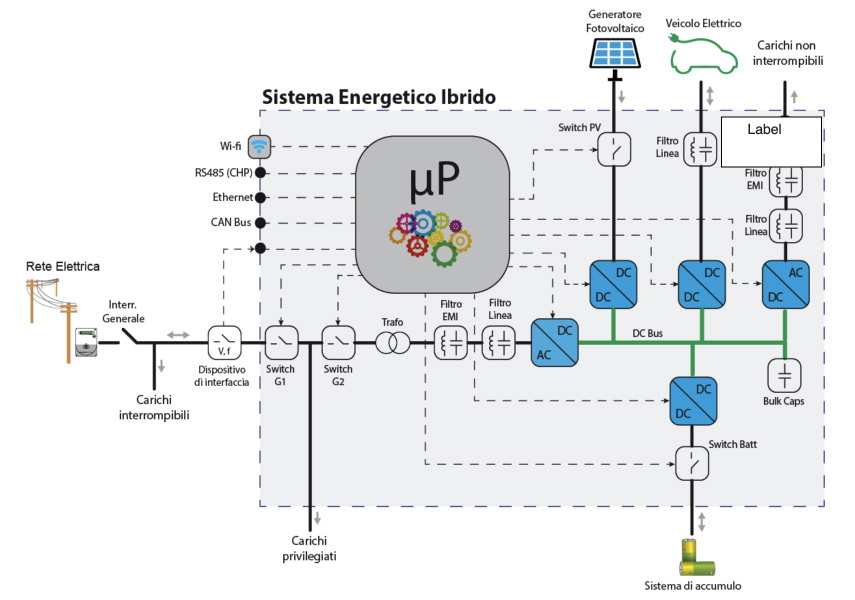
Hybrid Energy System (SEI)
An advanced and innovative system, able to manage multiple types of generation group and/or energy storage systems based on different technologies.
The main aim of SEI project falls within guideline of EU, the PNIEC, the PNR and the Smart Specialization Strategy Calabria, and share the same value to make the Europe citizen the main actors of “carbon free” energy model, during all energy transition phase.
SEI represents the technology for an efficient and integrated management of energy, also allowing companies to present themselves in the reference market sector with an innovative technological and digital solutions and from the point of view of functionality and performance better than what is already proposed.

Innovative requirements
SEI could be a valid tool to allow companies in the energy sector to present themselves in the reference market with an innovative solution

Development opportunities for companies
Great potential for development in the field of Smart Grids for companies in the energy sector and for the active management of end-users

Community Energy System
SEI represent the way to form Energy Communities in order to maximizing the use of RES generation according according to the self-consumption scheme
Our partners
Hybrid Energy System
SEI Architecture and Focus
- PRO RENEWABLE ENERGY COMMUNITY
- MODULAR AND FLEXIBLE ARCHITECTURE
- FUNCTIONALITY FOR NETWORK OPERATORS
PRO RENEWABLE ENERGY COMMUNITY
SEI is one of the enabling technologies that can be adopted in order to favor the energy transition, including the involvement of citizens to build aggregations such as renewable energy communities (RECs). Thanks to the RECs it is possible to achieve the objective of encouraging citizens to consume the energy produced by plants powered by RES (self-consumption) and belonging to the community itself.
European Green Deal
European climate legislation since to June 2021. The Member States have made a commitment to make the EU the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. To achieve this goal, they have pledged to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
RePowerEU
REPowerEU is the European Commission's plan to make Europe independent of Russian fossil fuels before 2030, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Energy sharing
Following the current energy market rules, it is possible maximize the share of energy produced by RES, managing the distributed technologies that supported the storage systems and RES generation systems.
Social and economic benefits
◉ Savings on bills
◉ Enhancement of shared energy
◉ Maximization of the use of RES generation
◉ Bonus to fight energy poverty
◉ Investments in social projects
Cultural benefits
Active participation of the community will be able to contribute to develop an innovative solution of common goods management, in the construction of new local development policies and in the experimentation of new welfare models that focus on the involvement of citizens.

MODULAR AND FLEXIBLE ARCHITECTURE
SEI is a complex and modular system of energy conversion and management able to run multiple types of generation sources and/or energy storage systems of different technologies, as well as the exchange and sharing of energy flows.
The system shows a modular architecture capable of extending "locally", connecting different devices to the base module, and widely, connecting multiple SEIs via their DC bus in order to create a DC microgrid or cross-connecting different systems through the internet. It starting from a basic module (user with photovoltaic system only - Prosumer), to then continue to integrate an energy storage system (user with PV + Storage - Prosumager)
DBS control
Decentralized control distributed based on voltage measurement on DC BUS by which all types of generation sources and/or storage systems are integrated on SEI
Modular configuration
The integration of a new generation or energy storage system to the DC BUS does not involve the implementation of new control logic. The DBS control is automatically adapted according to the new SEI configuration
DC microgrids
The working principle of DC microgrids is similar to the AC counterparts. The main is the DC bus network for interconnection instead of AC bus which interconnects the distributed generators and loads in the network.

PRO RENEWABLE ENERGY COMMUNITY
In a REC, one or more SEIs with integrated energy storage system can also be managed to provide system services to the grid operators such as
synthetic inertia, fast reserve, frequency regulation, primary, secondary and tertiary reserve, increase in demand in hours with excess production;
Network services such as
overcoming local «bottlenecks» due to RES, voltage regulation, service continuity (minimum level), exchange profile between the distribution and transmission networks, as well as local services such as arbitrage on energy prices producer, producer/consumer, reduction of imbalances, increase in self-consumption, continuity/quality of service.
- Synthetic inertia
The dynamic performance of the national Grid and the quality of the service will be compromised by the progressive decommissioning of the conventional thermal park. Thus, the need to have distributed systems that can contribute to the robustness of the network in terms of synthetic inertia. - Fast reserve
In recent years there has been a reduction in the frequency regulation power deriving from the modification of the production mix in favor of RES facilities which generally do not contribute to this regulation. To improve system stability, the introduction of a service characterized by a full activation time lower than that of the primary regulation is in an experimental phase. For this reason, the "Fast Reserve" is therefore intended as a service coordinated with the primary regulation to contribute to grid safety. - Frequency regulation (primary, secondary and tertiary)
In any electrical system, the power demand by users is balanced by the power fed into the grid by the generation plants. A constant frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) must be maintained during operation. When an instantaneous power imbalance occurs, a frequency transient is triggered in the system. To maintain stability and continuity in the functioning of the system, some generation groups are activated, typically thermal power stations with high mechanical inertia and rotating masses, which provide frequency regulation services. The Italian regulatory framework classifies frequency regulation services into primary, secondary and tertiary reserve regulation services. - Voltage regulation
The reduction of conventional thermal units connected to the grid will also have an impact on aspects related to voltage stability and the methods of regulating it. Also in this case, distributed voltage regulation resources will play a fundamental role, such as storage systems that can offer regulation capacity in terms of reactive power. - Peak shaving
Storage systems also play a major role in providing peak services shaving.
Their discharge capacity can be used to compensate for the energy demand exceeding a maximum reference value, providing benefits both for the utility company and for the end-user. - Load Levelling
Storage systems can mainly be operated with the maximum economic convenience for load- leveling applications (to compensate for the uneven distribution of the load during the various hours of the day) and therefore keep the absorbed power constant while simultaneously producing benefits, for the utility company (in terms of reduction of losses, leveling of voltage values, deferral of power supply line upgrading works, increase in the useful life of cables) and for the end user (essentially in terms of reduction in the cost of consumption of electric energy).
Sign up for the newsletter



